Please note, this blog entry is from a previous course. You might want to check out the current one.
Instead of opening urls in Safari, display them in your application by segueing to a controller with a UIWebView. You’ll have to provide at least a little bit of “browser control” UI to go along with it (e.g. a “back button”).
Add a new view controller to the storyboard. Add a egue from the mentions table view controller to the new controller (be careful, not from a cell, but from the controller itself!). Add a web view, an activity indicator and a back button (don’t forget constraints for autolayout):
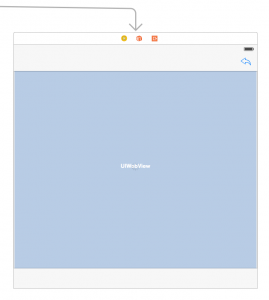
Create a new class for the new controller and connect them. Add outlets for the web view and the activity indicator. Add an action for the back button:
@IBOutlet weak var webView: UIWebView!
@IBOutlet weak var spinner: UIActivityIndicatorView!
@IBAction func back(sender: UIBarButtonItem) {
}
Add a public property to hold the URL. When it gets set and it has a chance to appear on screen, start loading the URL, or at least when the view did load:
var url: NSURL? {
didSet {
if view.window != nil {
loadURL()
}
}
}
private func loadURL() {
if url != nil {
webView.loadRequest(NSURLRequest(URL: url!))
}
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
webView.scalesPageToFit = true
loadURL()
}
Make the the controller the delegate of the web view and use its delegate method to start and stop the activity indicator depending on the status of the downloads:
class WebViewController: UIViewController, UIWebViewDelegate {
override func viewDidLoad() {
...
webView.delegate = self
...
}
var activeDownloads = 0
func webViewDidStartLoad(webView: UIWebView) {
activeDownloads++
spinner.startAnimating()
}
func webViewDidFinishLoad(webView: UIWebView) {
activeDownloads--
if activeDownloads < 1 {
spinner.stopAnimating()
}
}
}
… and an actual activity to the action when the back button gets pressed:
@IBAction func back(sender: UIBarButtonItem) {
webView.goBack()
}
In the mentions table view controller – where up to now the safari was called – perform the new segue and set the URL of the web view controller:
private struct Storyboard {
...
static let WebSegueIdentifier = "Show URL"
}
override func shouldPerformSegueWithIdentifier(identifier: String?, sender: AnyObject?) -> Bool {
...
if url.hasPrefix("http") {
performSegueWithIdentifier(Storyboard.WebSegueIdentifier, sender: sender)
return false
}
...
}
override func prepareForSegue(segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: AnyObject?) {
...
} else if identifier == Storyboard.WebSegueIdentifier {
if let wvc = segue.destinationViewController as? WebViewController {
if let cell = sender as? UITableViewCell {
if let url = cell.textLabel?.text {
wvc.url = NSURL(string: url)
}
}
}
}
...
}
The complete code for extra task #4 is available on GitHub.
![By Wilgengebroed on Flickr [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://cs193p.m2m.at/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/cs193p-Project-4-Assignment-4-Extra-Task-4-825x510.jpg)